Museum
Project role: Chief Designer and coordinator for I.M. Pei – Architect
Commissioned by: Qatar Museum Authority
Location: Doha, Qatar
Completion 2006, opening 2008
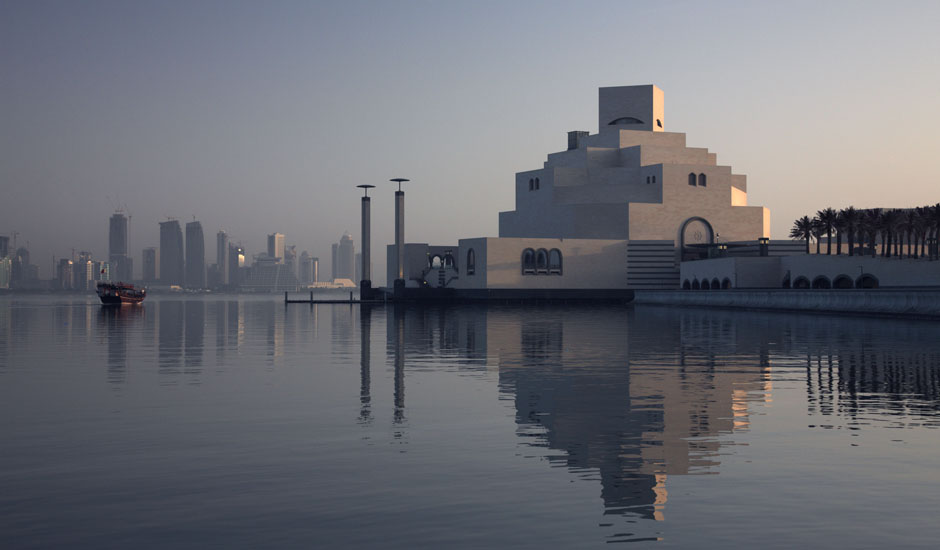
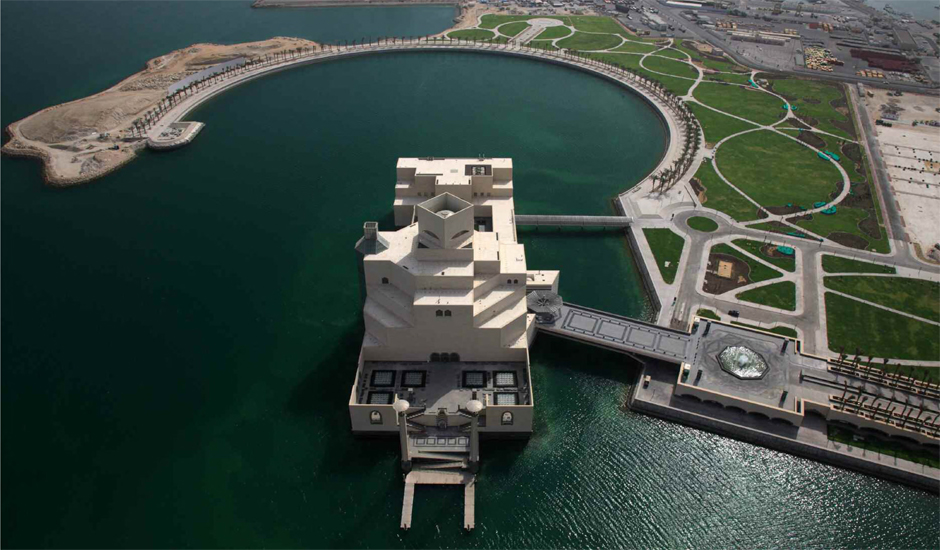
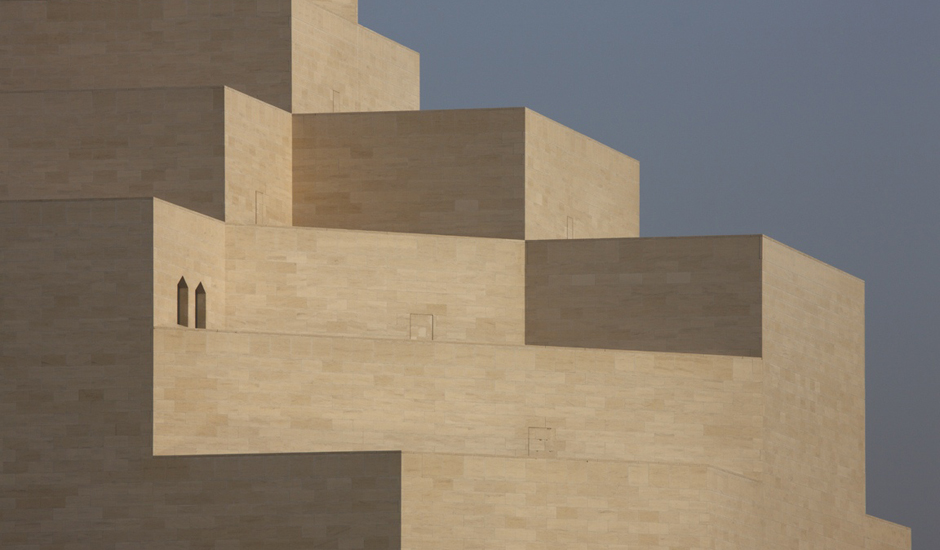
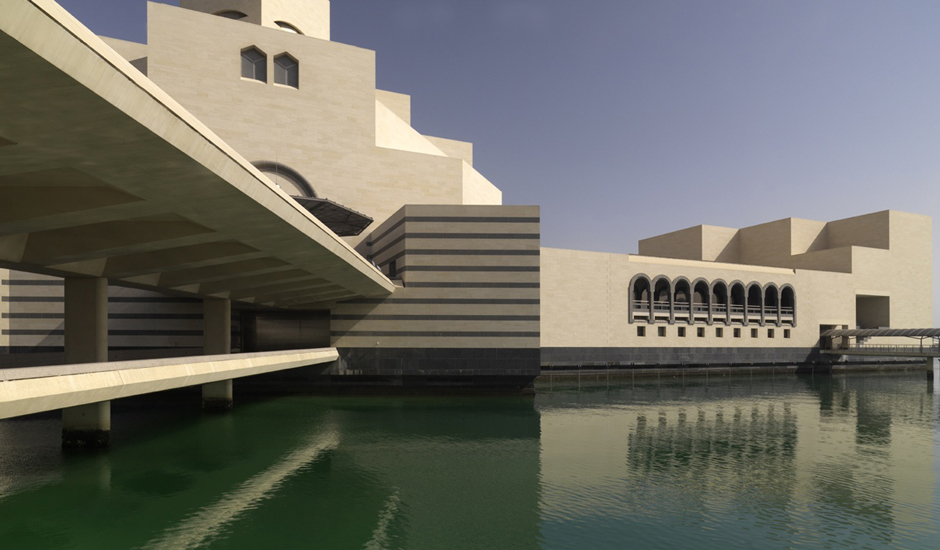
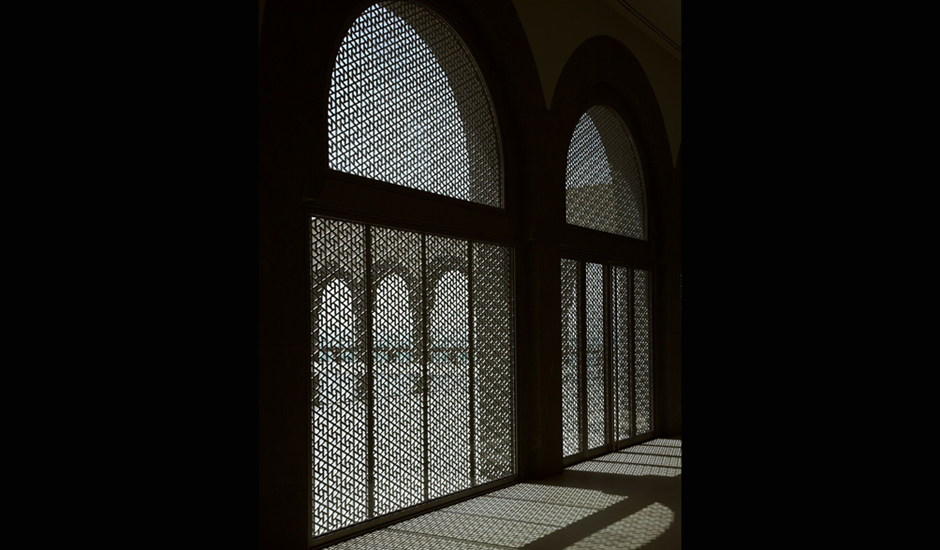
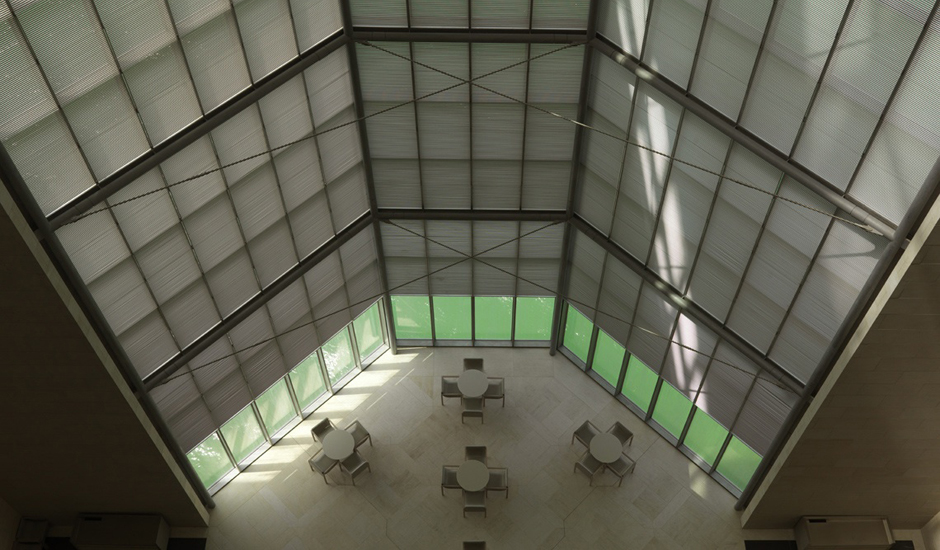
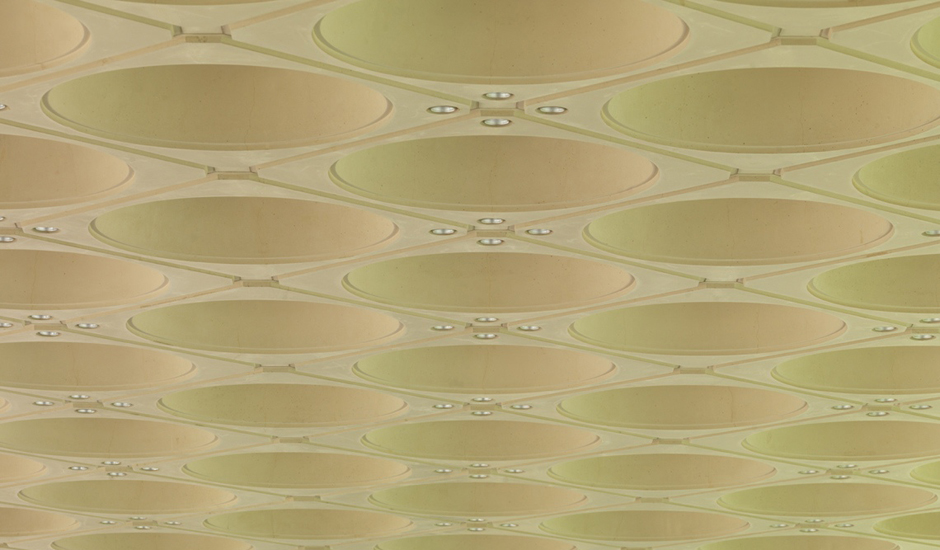
The 3600m² museum is situated on the waters of the Persian Gulf in Doha, Qatar. Today, the building stands 60 m (195 ft) off Doha’s Corniche on an island made of reclaimed land, and is connected to shore by two pedestrian bridges and a vehicular bridge. A C-shaped peninsula and park area on the shoreline behind the Museum offer shelter and a picturesque backdrop. The stone-clad Museum is composed of a five-story Main Building and a two-story Education Wing, which are connected across a central courtyard.
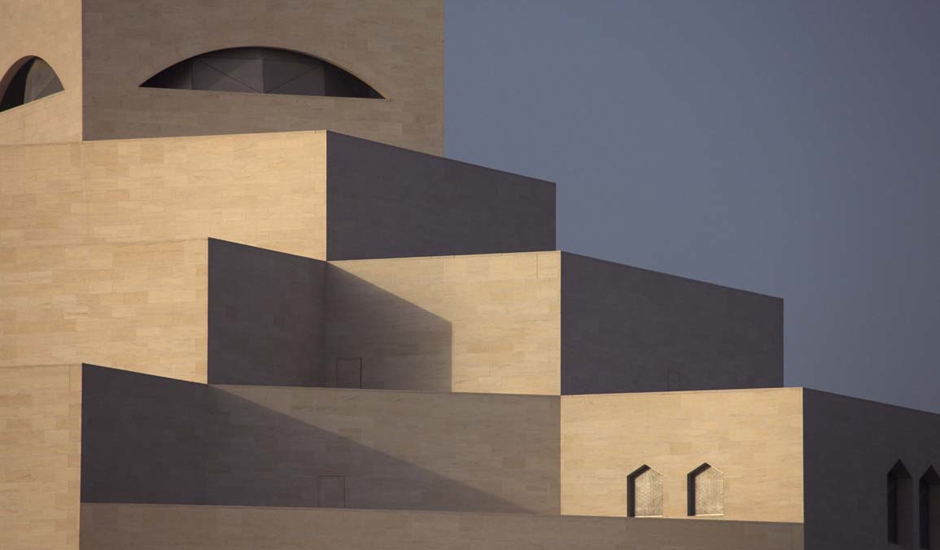
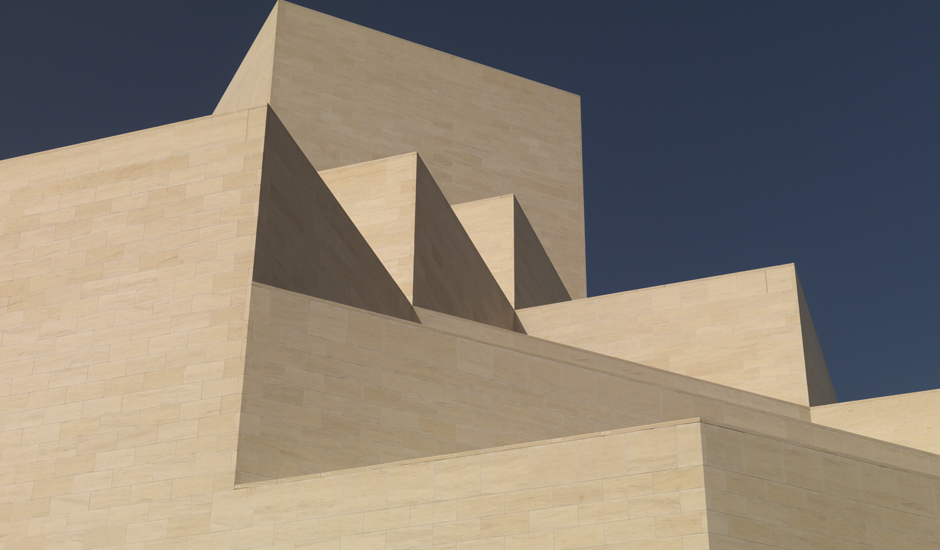
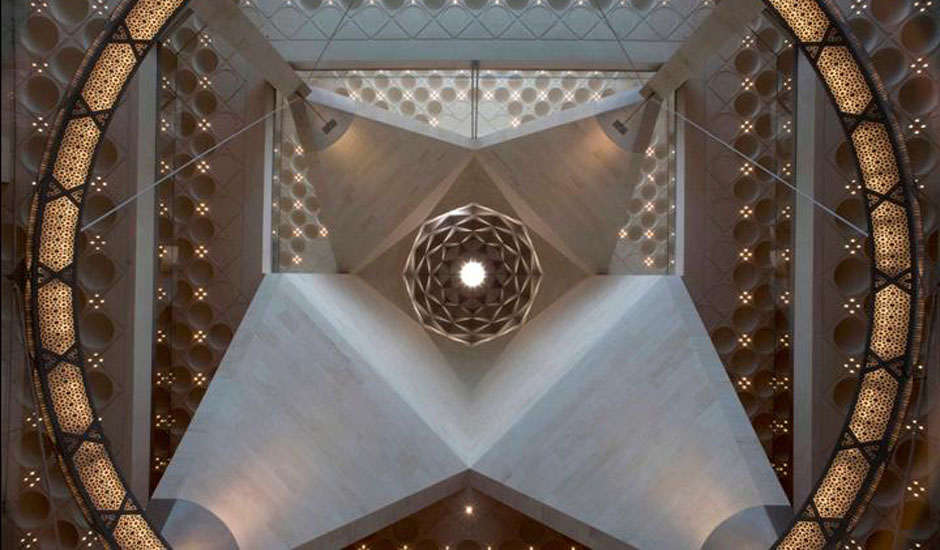
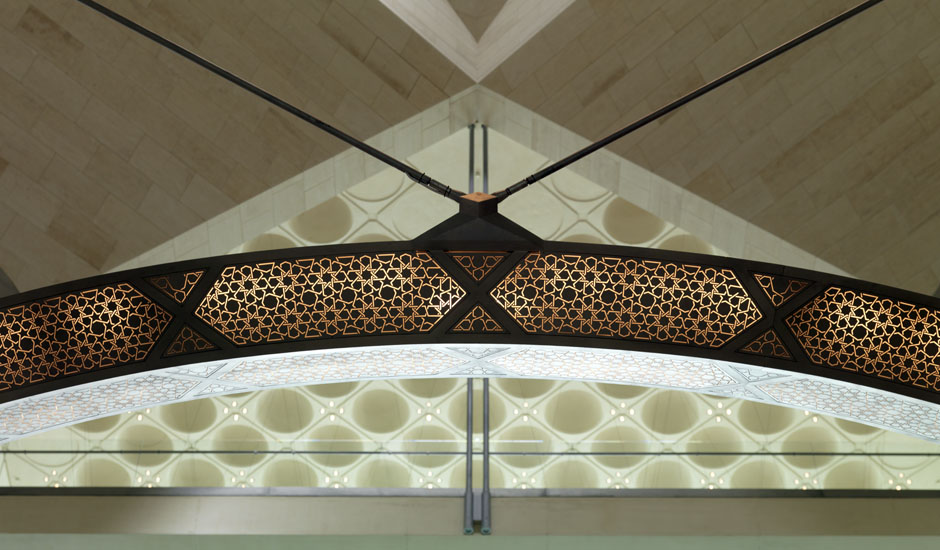
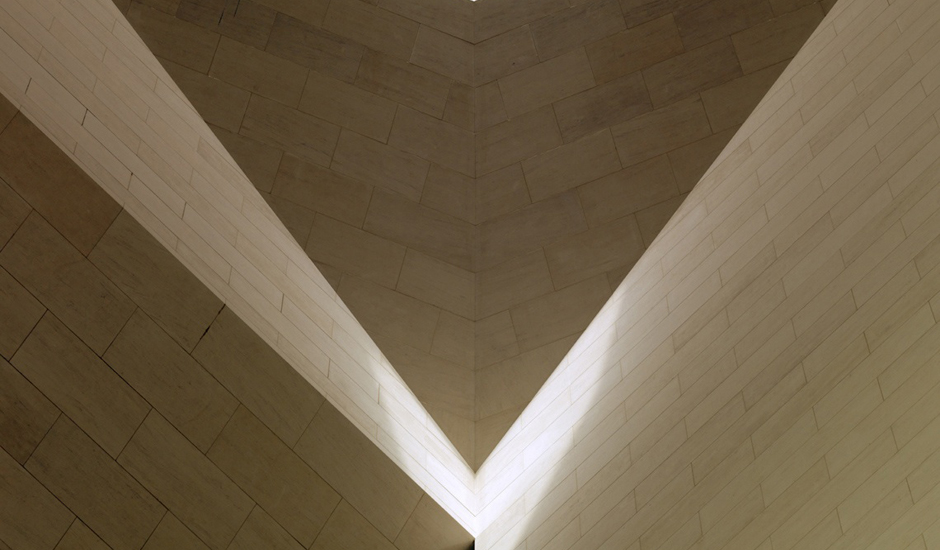
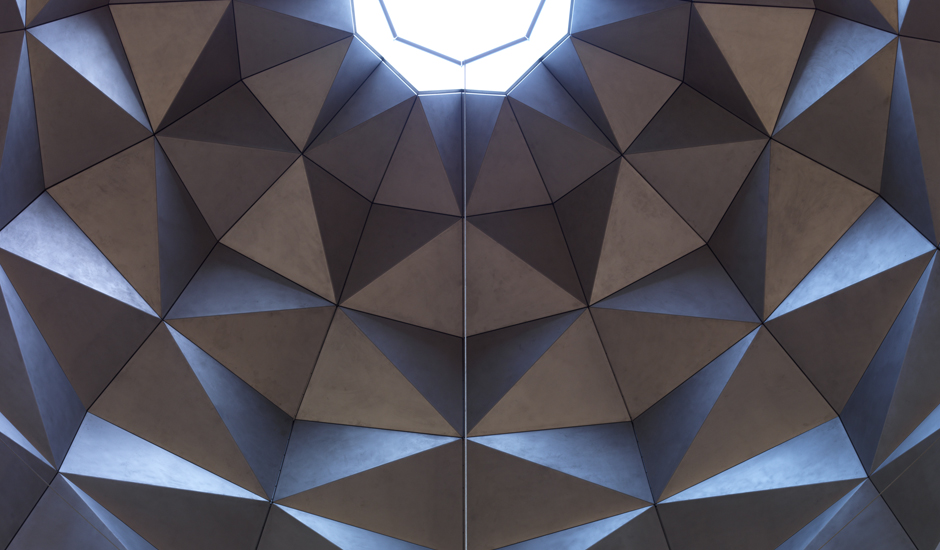
The Main Building’s angular volumes step back progressively as they rise around a 54-m-high (177 ft) central domed atrium. The dome is concealed from outside view by the walls of a central tower. A sheet of glass rises to a height of 45 m (148 ft) on the north side of the Museum offering views of the Gulf and West Bay area of Doha from all five floors of the atrium.
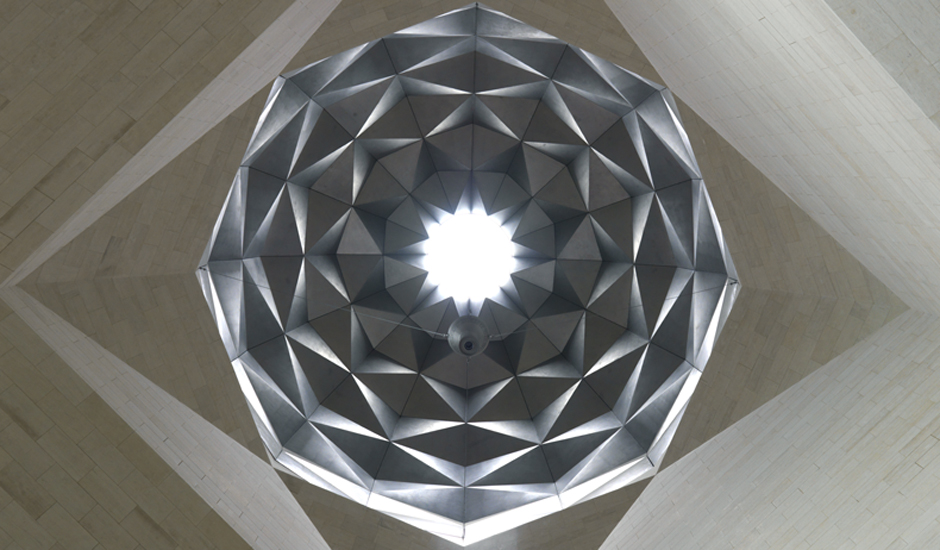
At the top of the atrium is the circular oculus of a stainless steel dome, which captures facets of patterned light. The form of the dome changes as the structure descends, so its perimeter becomes an octagon and then a square, which in turn is transformed into four triangular column supports.
http://www.mia.org.qa/en/